The Lion King | 17
T
he area that today is
Senegal was once part of
the West African Empire of
Mali, Ghana, and Tekrur. The
country takes its name from the
river that runs along its northern
and eastern borders, forming
the frontier with Mauritania and
Mali. A poetic etymology from
the Wolof people states that the
name derives from the local term
Sunugal, meaning “our dugout
canoe” (everyone is in the same
boat). The Republic of Senegal
became independent in 1960
after three centuries of French
colonial rule.
The French colonies of Senegal
and the French Sudan were
merged in 1959 and granted
their independence as the Mali
Federation in 1960. The union
broke up after only a few months.
Senegal joined with The
Gambia to form the nominal
confederation of Senegambia in
1982. The envisaged integration
of the two countries was never
carried out, and the union was
dissolved in 1989.
GEOGRAPHY
Senegal, situated on the western
tip of Africa, covers an area
of 76,000 square miles (196,781
square kilometers). It is bordered
on the north by Mauritania, on
the east by Mali, on the south
by Guinea and Guinea-Bissau,
and on the west by the Atlantic
Ocean. The long, narrow
Republic of the Gambia is
approximately two hundred miles
long, surrounded by Senegal’s
southern region.
SYMBOL
The national anthem, flag
and its colors have been used
as national symbols since
independence.
The national flag has bands of
green, yellow, and red. A green
five-pointed star appears in the
center of the yellow band. The
color green symbolizes the forest
and hope. Yellow stands for the
savanna and red for the blood
spilled in the fight for liberty
Country Focus
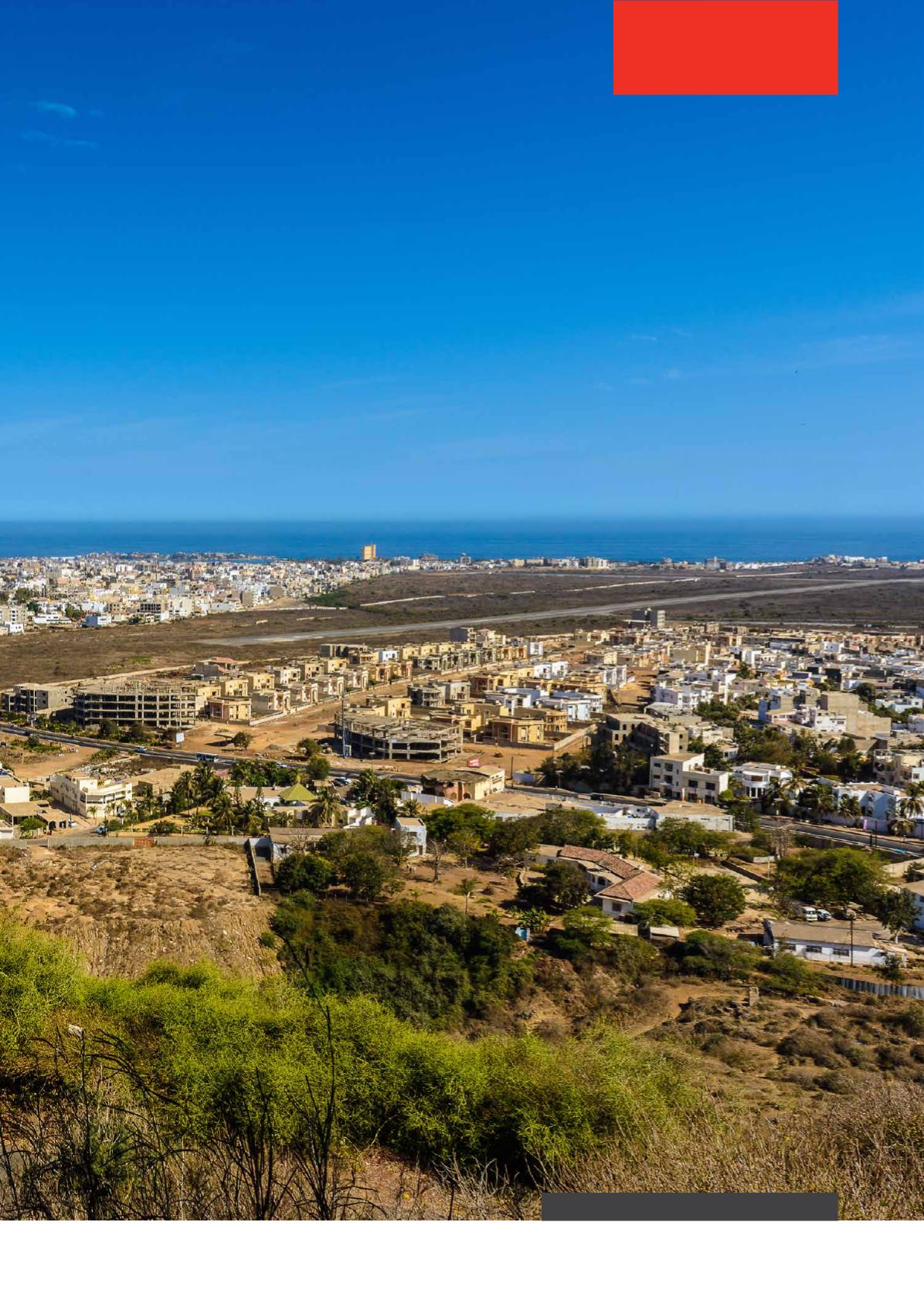
Panorama of Dakar, the capital of Senegal